Jean Piaget's stages of Cognitive Development
4 stages of Cognitive Development
- Sensorimotor
- Preoperational
- concrete operational
- formal operational
To View :
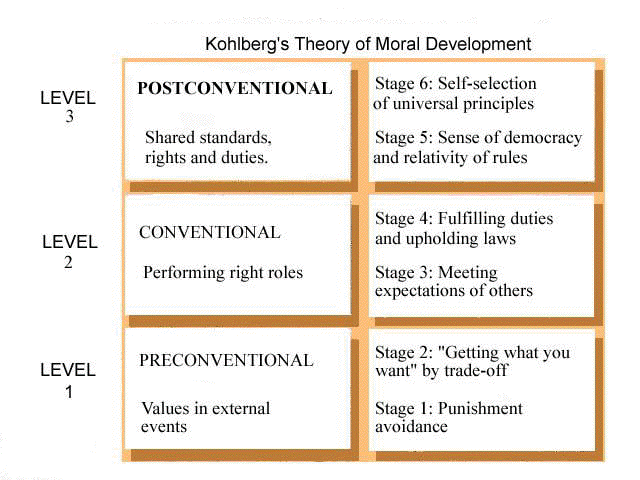
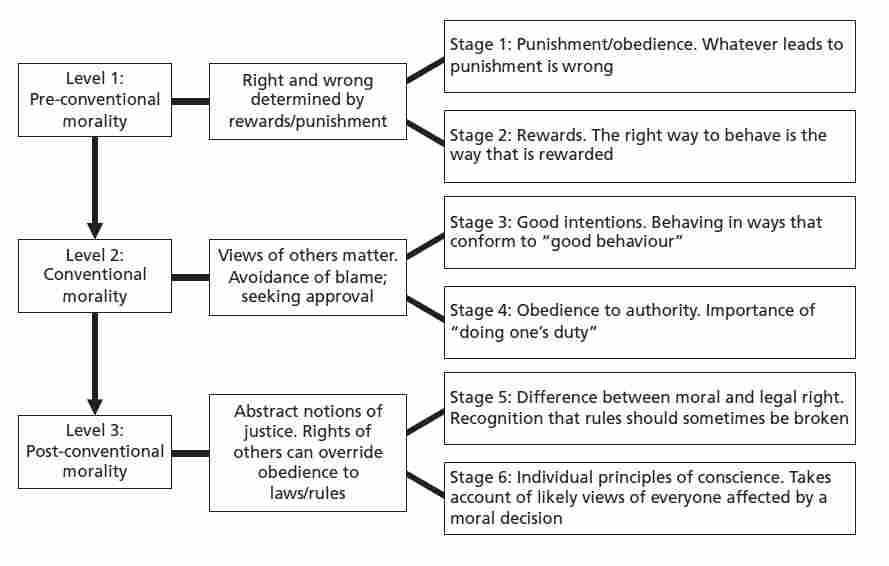
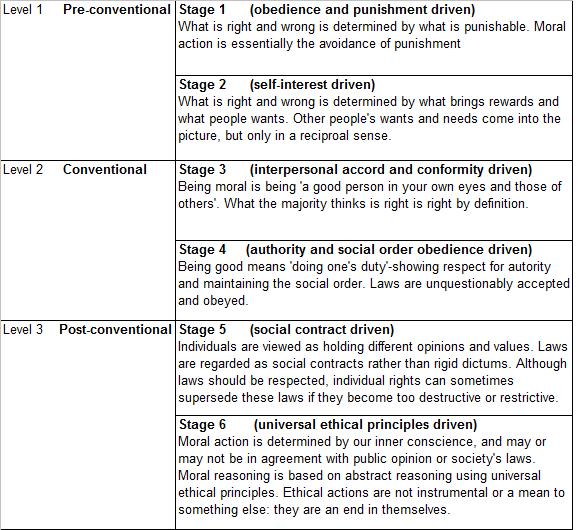
http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/jean-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development.html#lessonLawrence Kholberg's stages of Moral Development
To view :
Carol Gilligan theory of Moral Development
To view :
http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/carol-gilligans-theory-of-moral-development.html#lessonErickson's 8 stages of Maturation
to view :
Freud's Psychosexual stages of Development
to view :
Margret Mahler's Stages of Development
 |
| Margret Mahler |
Refer :
http://www.powershow.com/view1/d68fd-ZDc1Z/Development_of_Self_powerpoint_ppt_presentation
http://www.childdevelopmentmedia.com/margaret-mahler-and-the-separation-individuation-theory.html
http://www.childdevelopmentmedia.com/margaret-mahler-and-the-separation-individuation-theory.html
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
to view :
Alfred Adler's birth order
to view :
Jane Loevinger's stages of ego development
 |
| Jane Loevinger |
2. Impulsive : difference between self and mother, fixation with sexul and aggressive drives, implosive and exploitative and dependent
3. Opportunistic: child tries to manipulate and control others, follows rules and moralities when it is conveniently advantageous to them
4. Conformist : child develops trust, becomes very self conscious of their appreance, how others see them and their personal possessions, rules are somewhat internalized
5. conscientious : child internalizes morality regulated by ethical imperatives, disobedience results in feelings of guilt, relationship with others are intense and accountable, internal feelings and success pre occupy their thoughts
6. Autonomous : constant thoughts about self identity and fulfillment, maintaining independence in relationships, learning to deal with and accept personal conflicts, differences with others and controlling impulses
7. Integrated : grandiose or unattainable ideas from childhood are replaced, appreciate individuality in personal relationships, reconciliation of conflicts, constant thoughts of attaining an integrated identity
8. Self protective (transition stage between stage 1 and 2)
9. Self aware :(transition stage between 4 and 5 )
refer :
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Loevinger's_stages_of_ego_developmentRobert Havinghurst theory of developmental task
 |
| Robert Havinghurst |
Six stages of Developmental tasks
- Infancy and early childhood (0-6) - learning to walk, take solid foods, talk, control elimination of body waste, sex differences and sexual modesty, achieving physiological stability and forming simple concepts of social and physical reality, learning to relate oneself to parent, sibling and other people, learning to distinguish between right and wrong and developing a conscience
- Middle Childhood (age 6-12) - learning physical skills necessary for ordinary games, building wholesome attitude towards oneself as a growing organism, learning to get along with age mates, learning appropriate masculine and feminine social role, developing fundamental skills in reading writing and calculation, developing concepts necessary for everyday living, developing conscience, morality and a scale of values, achieving personal independence
- Adolescence(12-18) - achieving new and more mature relations with age mates of both sexes, achieving a masculine or feminine social role, accepting one's physique and using the body effectively, achieving emotional independence of parents and other adults, achieving assurance of economic independence, selecting and preparing for an occupation, preparing for marriage and family life, developing intellectual skills and competence necessary for civic competence, desiring and achieving socially responsible behavior, acquiring a set of values and an ethical system as a guide to behavior
- Early Adulthood (18-30) - selecting a mate,learning to live with a partner, starting family , rearing children, managing home, getting started in occupation, taking on civic responsibility, finding a congenial social group
- Middle Age (30-60) achieving adult civic and social responsibility, establishing and maintaining an economic standard of living, assisting teen age children to become responsible and happy adults, developing adult leisure time activities, relating oneself to one's spouse as a person, accepting and adjusting to physiological changes of middle age, adjusting to aging parents
- Later Maturity (past 60) - adjusting to decreasing physical strength and health, adjustment to retirement and reduced income, adjusting to death of a spouse, establishing an explicit affiliation with one's age group, meeting social and civic obligations, establishing satisfactory physical living arrangements
http://www.slideshare.net/teachingandmore882/robert-j-8202628
David levinnson's Life structure or Adult Development theory
to refer :
Noam CHomsky language development
 |
| Noam Chomsky |
to view:
Benjamin Whorf linguistic relativity
 |
| Benjamin Lee Whorf |














No comments:
Post a Comment